OpenFOAMで実装されている離散化スキームである QUICK について解説する
有限体積法による離散化
コンピュータで偏微分方程式を解くためには,計算格子上に偏微分方程式を離散化する必要がある
OpenFOAMで用いられている離散化手法である有限体積法を用いると,輸送方程式,発散,勾配は次のように離散化できる
(輸送方程式)
\begin{align}
&\frac{\partial}{\partial t}(\rho\phi)
+\nabla\cdot(\rho\mathbf{u}\phi)
=s
+\nabla\cdot\left(\Gamma\nabla \phi\right) \\
\\ \rightarrow \quad
&\frac{\partial}{\partial t}(\rho_{_{P}}\phi_{_{P}}V_{_{P}})
+\sum_{f}{F\phi_{f}}
=s_{_{P}}V_{_{P}}
+\sum_{f}{\Gamma_{f}\left|S_{f}\right|\frac{\phi_{_{N}}-\phi_{_{P}}}{|\mathbf{x}_{_{N}}-\mathbf{x}_{_{P}}|}}
\end{align}
(発散)
\begin{equation}
\nabla\cdot\phi \quad \rightarrow \quad \sum_{f}\mathbf{S}_{f}\cdot\phi_{f}
\end{equation}
(勾配)
\begin{equation}
\nabla\phi \quad \rightarrow \quad \sum_{f}\mathbf{S}_{f}\phi_{f}
\end{equation}
ここで,添え字\(_P\),\(_N\),\(_f\) はそれぞれ注目セル\(P\),隣接セル\(N\),注目セルと隣接セルの境界面\(f\)における代表値であることを表し,\(\phi\)は何かしらの物理量,\(V\)はセル体積,\(\Gamma\)は拡散係数である
また,\(|S_{f}|\)は注目セルと隣接セルの境界面の面積,\(\mathbf{S}_{f}\)は境界面に垂直で境界面の面積\(|S_{f}|\)を大きさに持つ法線ベクトルであり,\(\sum_{f}\)はセルがもつすべての面に対する総和を表す
上記3つの離散化を見てみると未知数は\(\phi_{f}\)のみであり,有限体積法の離散化は「境界面上の代表値\(\phi_{f}\)をどのように補間するか」という点に集約されていることがわかる
セルが不規則に配置されている非構造格子では,\(\phi_{f}\)の離散化に使える値は注目セル\(P\)の代表値\(\phi_{_{P}}\)と隣接セル\(N\)の代表値\(\phi_{_{N}}\)の2つのみである
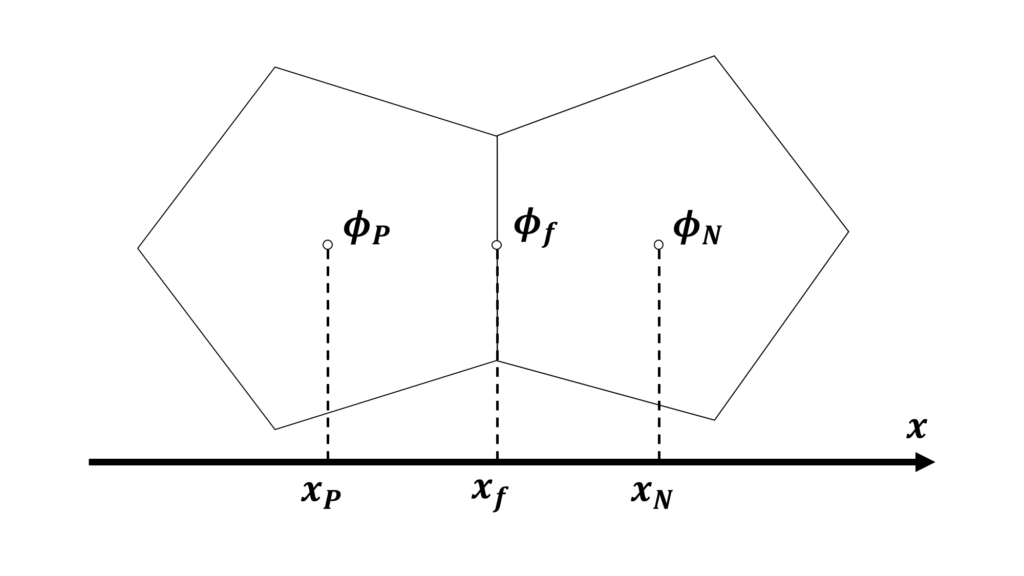
\(\phi_{f}\)を\(\phi_{_P}\)と\(\phi_{_N}\)によって補間すると次の連立方程式が得られる
\begin{equation}
\mathbf{A}_{_{P}}\phi_{_{P}}+\sum{\mathbf{A}_{_N}\phi_{_N}}
=\mathbf{b}
\end{equation}
\(\mathbf{A}\)や\(\mathbf{b}\)の具体的な値を決定するのは偏微分方程式の離散化に用いられた離散化スキームであり,離散化スキームの精度や性質によって計算の安定性や結果の精度は大きく変化する
↓離散化の導出についてはこちら
QUICK
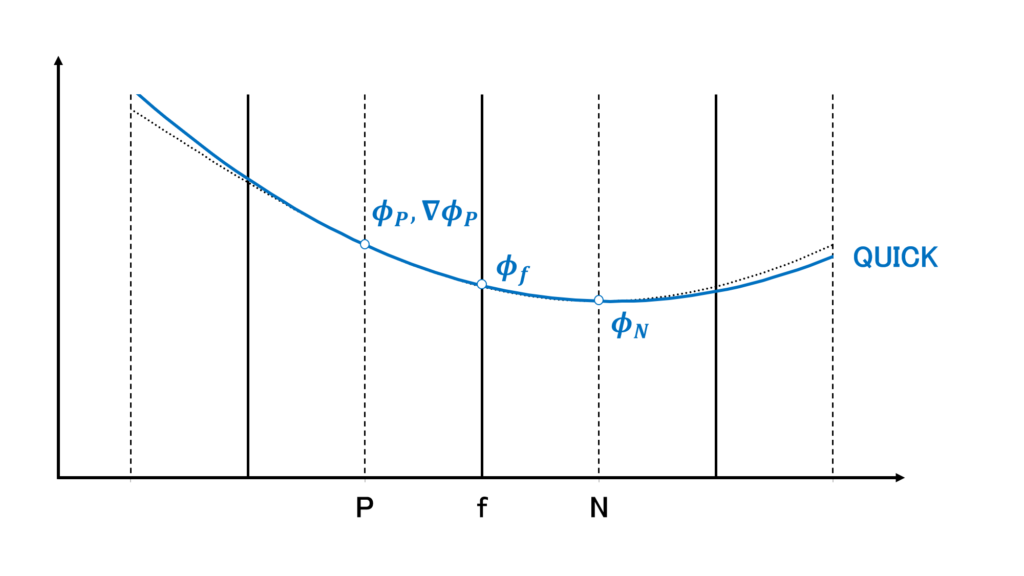
QUICK(Quadratic Upstream Interpolation for Convective Kinematics)は補間としては3次精度であり,少しだけ数値粘性の力を借りたいときの速度の対流項としてよく設定される
QUICKでは,質量流束\(F=\mathbf{u}_{f}\cdot\mathbf{S}_{f}\) の符号で上流側を判断し,上流側の値,上流側の点における勾配,下流側の値の3つを使って,\(\phi_{f}\)を次のように補完する
\begin{equation}
\phi_{f}=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}
\frac{3}{4}\phi_{_{P}}+\frac{1}{4}\phi_{_{N}}
+\frac{1}{4}\left(\nabla\phi\right)_{P}\cdot\left(\mathbf{x}_{N}-\mathbf{x}_{P}\right)
& \left(F>0\right) \\
\frac{1}{4}\phi_{_{P}}+\frac{3}{4}\phi_{_{N}}
+\frac{1}{4}\left(\nabla\phi\right)_{N}\cdot\left(\mathbf{x}_{P}-\mathbf{x}_{N}\right)
& \left(F<0\right) \\
\end{array}\right.
\end{equation}
↓詳しくはこちら
OpenFOAMにおける実装
OpenFOAMでは,QUICKはTVDスキームの枠組みを用いて以下のように実装される
\begin{align}
&\phi_{f}=w\left(\phi_{_{P}}-\phi_{_{N}}\right)+\phi_{_{N}} \tag{1} \\ \\
&w=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}
\psi w_{_{CD}}+\left(1-\psi\right) & \left(F>0\right) \\
\psi w_{_{CD}}-\left(1-\psi\right) & \left(F<0\right) \\
\end{array}\right. \tag{2} \\ \\
&\psi=\frac{\phi_{f}-\phi_{_{UD}}}{\phi_{_{CD}}-\phi_{_{UD}}} \tag{3} \\ \\
&\phi_{f}=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}
\frac{1}{2}\left\{\phi_{_{CD}}+\phi_{_P}+\left(1-w_{_{CD}}\right)\left(\mathbf{x}_{N}-\mathbf{x}_{P}\right)\cdot\left(\nabla\phi\right)_{P}\right\}
& \left(F>0\right) \\
\frac{1}{2}\left\{\phi_{_{CD}}+\phi_{_N}-w_{_{CD}}\left(\mathbf{x}_{N}-\mathbf{x}_{P}\right)\cdot\left(\nabla\phi\right)_{N}\right\}
& \left(F<0\right) \\
\end{array}\right. \tag{4}
\end{align}
ここで,\(\phi_{_{UD}}\)は風上差分(upwind)による境界面の補間値,\(\phi_{_{CD}}\)は中心差分(linear)による境界面の補間値であり,\(w_{_{CD}}\)は中心差分に用いる重み係数である
\(\psi\)は流束制限関数(flux limiter function)と呼ばれ,TVDスキームに用いられる関数である
境界面上の補間値
\(F>0\)として,\(\phi_{_{CD}}=w_{_{CD}}\phi_{_P}+\left(1-w_{_{CD}}\right)\phi_{_N}\) を(4)に代入する
\begin{align}
&\phi_{f}=\frac{1}{2}\left\{\phi_{_{CD}}+\phi_{_P}+\left(1-w_{_{CD}}\right)\left(\mathbf{x}_{N}-\mathbf{x}_{P}\right)\cdot\left(\nabla\phi\right)_{P}\right\} \\
\\ \rightarrow \quad
&\phi_{f}=\frac{1}{2}\left\{w_{_{CD}}\phi_{_P}+\left(1-w_{_{CD}}\right)\phi_{_N}+\phi_{_P}+\left(1-w_{_{CD}}\right)\left(\mathbf{x}_{N}-\mathbf{x}_{P}\right)\cdot\left(\nabla\phi\right)_{P}\right\} \\
\\ \rightarrow \quad
&\phi_{f}=\frac{1+w_{_{CD}}}{2}\phi_{_P}+\frac{1-w_{_{CD}}}{2}\phi_{_N}+\frac{1-w_{_{CD}}}{2}\left(\mathbf{x}_{N}-\mathbf{x}_{P}\right)\cdot\left(\nabla\phi\right)_{P} \\
\end{align}
\(w_{_{CD}}=\frac{1}{2}\)とすると,\(F>0\)におけるQUICKの式が得られることがわかる
\begin{equation}
\phi_{f}=\frac{3}{4}\phi_{_P}+\frac{1}{4}\phi_{_N}+\frac{1}{4}\left(\nabla\phi\right)_{P}\cdot\left(\mathbf{x}_{N}-\mathbf{x}_{P}\right) \\
\end{equation}
流束制限関数
TVDスキームとは,高精度だが発散しやすい中心差分と安定だが解が減衰する風上差分を混合することによって,高精度で安定な差分を構成しようとするスキームである
中心差分と風上差分の混合を調整する関数として流束制限関数\(\psi\)を導入すると,境界面上における補間値は次のように表される
\begin{equation}
\phi_{f}=\phi_{_{UD}}+\psi\left(\phi_{_{CD}}-\phi_{_{UD}}\right) \tag{i}
\end{equation}
整理すると(3)が得られる
\begin{equation}
\psi=\frac{\phi_{f}-\phi_{_{UD}}}{\phi_{_{CD}}-\phi_{_{UD}}} \tag{3}
\end{equation}
重み係数
\(F>0\)として,(i)に \(\phi_{_{CD}}=w_{_{CD}}\phi_{_P}+\left(1-w_{_{CD}}\right)\phi_{_N}\) と \(\phi_{_{UD}}=\phi_{_P}\) 代入する
\begin{align}
&\phi_{f}=\phi_{_{UD}}+\psi\left(\phi_{_{CD}}-\phi_{_{UD}}\right) \\
\\ \rightarrow \quad
&\phi_{f}=\phi_{_P}+\psi\left(w_{_{CD}}\phi_{_P}+\left(1-w_{_{CD}}\right)\phi_{_N}-\phi_{_P}\right) \\
\\ \rightarrow \quad
&\phi_{f}=\left\{1-\left(1-w_{_{CD}}\right)\psi\right\}\phi_{_P}+\left(1-w_{_{CD}}\right)\psi\phi_{_N} \\
\end{align}
\(w=1-\left(1-w_{_{CD}}\right)\psi=\psi w_{_{CD}}+\left(1-\psi\right)\)とすると,(1)が得られる
\begin{align}
&\phi_{f}=w\phi_{_P}+\left(1-w\right)\phi_{_N} \\
\\ \rightarrow \quad
&\phi_{f}=w\left(\phi_{_P}-\phi_{_N}\right)+\phi_{_N} \tag{1} \\
\end{align}
参考
≫User Guide: QUICK divergence scheme - OpenFOAM
実装は主に以下のファイルに記述されている
≫surfaceInterpolationScheme.C:離散化スキームの親クラス
≫limitedSurfaceInterpolationScheme.C:TVDスキームのクラス
≫QUICK.H:子クラス
surfaceInterpolationScheme.C で補間式(1), limitedSurfaceInterpolationScheme.C で重み係数(2),QUICK.H で流束制限関数(3)が計算されている
それでは1つずつ確認していく
流束制限関数
流束制限関数は QUICK.H の中の limiter() で次のように定義されている
\begin{align}
&\phi_{f}=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}
\frac{1}{2}\left\{\phi_{_{CD}}+\phi_{_P}+\left(1-w_{_{CD}}\right)\left(\mathbf{x}_{N}-\mathbf{x}_{P}\right)\cdot\left(\nabla\phi\right)_{P}\right\}
& \left(F>0\right) \\
\frac{1}{2}\left\{\phi_{_{CD}}+\phi_{_N}-w_{_{CD}}\left(\mathbf{x}_{N}-\mathbf{x}_{P}\right)\cdot\left(\nabla\phi\right)_{N}\right\}
& \left(F<0\right) \\
\end{array}\right. \tag{4} \\ \\
&\psi=\frac{\phi_{f}-\phi_{_{UD}}}{\phi_{_{CD}}-\phi_{_{UD}}} \tag{3} \\ \\
\end{align}
scalar phiCD = cdWeight*phiP + (1 - cdWeight)*phiN; // 中心差分による境界面上の補間値
scalar phiU, phif;
if (faceFlux > 0) // F>0
{
phiU = phiP; // 風上差分による境界面上の補間値
phif = 0.5*(phiCD + phiP + (1 - cdWeight)*(d & gradcP)); // QUICKによる境界面上の補間値
}
else // F<0
{
phiU = phiN;
phif = 0.5*(phiCD + phiN - cdWeight*(d & gradcN));
}
// Calculate the effective limiter for the QUICK interpolation
scalar QLimiter = (phif - phiU)/stabilise(phiCD - phiU, SMALL); // 流束制限関数の計算
// Limit the limiter between upwind and downwind
return max(min(QLimiter, 2), 0);
max(min(QLimiter, 2), 0) はTVDスキームに関する操作だと考えられるがよくわからない
limiter() に与えられる引数は,LimitedScheme.C の calcLimiter() で次のように与えられている
tmp<GradVolFieldType> tgradc(fvc::grad(lPhi)); // phiの勾配
const GradVolFieldType& gradc = tgradc();
const surfaceScalarField& CDweights = mesh.surfaceInterpolation::weights(); // 中心差分に用いられる重み係数
const labelUList& owner = mesh.owner(); // 注目セルPのインデックス
const labelUList& neighbour = mesh.neighbour(); // 隣接セルNのインデックス
const vectorField& C = mesh.C(); // セルを代表する点の座標
scalarField& pLim = limiterField.primitiveFieldRef();
forAll(pLim, face)
{
label own = owner[face]; // 境界面fに隣接するセルPのインデックス
label nei = neighbour[face]; // 境界面fに隣接するセルNのインデックス
pLim[face] = Limiter::limiter
(
CDweights[face],
this->faceFlux_[face], // 質量流束
lPhi[own],
lPhi[nei],
gradc[own],
gradc[nei],
C[nei] - C[own] // セルPとセルNの代表点を結ぶベクトル
);
}重み係数
重み係数は limitedSurfaceInterpolationScheme.C の中の weights() で次のように定義されている
\begin{equation}
w=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}
\psi w_{_{CD}}+\left(1-\psi\right) & \left(F>0\right) \\
\psi w_{_{CD}}-\left(1-\psi\right) & \left(F<0\right) \\
\end{array}\right. \tag{2}
\end{equation}
// Note that here the weights field is initialised as the limiter
// from which the weight is calculated using the limiter value
surfaceScalarField& Weights = tLimiter.ref();
scalarField& pWeights = Weights.primitiveFieldRef(); // 流束制限関数
forAll(pWeights, face) // 重み係数の計算
{
pWeights[face] =
pWeights[face]*CDweights[face]
+ (1.0 - pWeights[face])*pos0(faceFlux_[face]);
}≫limitedSurfaceInterpolationScheme.C
pos0() は Scalar.H で次のように定義されている
//- Return 1 if s is greater_equal zero, or otherwise 0
inline Scalar pos0(const Scalar s)
{
return (s >= 0)? 1: 0;
}weights() は limitedSurfaceInterpolationScheme.H で次のように宣言されている
//- Return the interpolation weighting factors for the given field,
// by limiting the given weights with the given limiter
tmp<surfaceScalarField> weights
(
const GeometricField<Type, fvPatchField, volMesh>&,
const surfaceScalarField& CDweights, // 中心差分で用いる重み係数
tmp<surfaceScalarField> tLimiter // 流束制限関数
) const;
補間式
補間式は surfaceInterpolationScheme.C の中の dotInterpolate() で次のように定義されている
\begin{align}
&\phi_{f}=w\left(\phi_{_{P}}-\phi_{_{N}}\right)+\phi_{_{N}}
\end{align}
typedef typename Foam::innerProduct<typename SFType::value_type, Type>::type
RetType;
const surfaceScalarField& lambdas = tlambdas(); // 重み係数
const Field<Type>& vfi = vf; // phi
const scalarField& lambda = lambdas;
const fvMesh& mesh = vf.mesh();
const labelUList& P = mesh.owner(); // 注目セルPのインデックス
const labelUList& N = mesh.neighbour(); // 隣接セルNのインデックス
tmp<GeometricField<RetType, fvsPatchField, surfaceMesh>> tsf // 補完した値を入れるための変数
(
new GeometricField<Type, fvsPatchField, surfaceMesh>
(
IOobject
(
"interpolate("+vf.name()+')',
vf.instance(),
vf.db()
),
mesh,
vf.dimensions()
)
);
GeometricField<RetType, fvsPatchField, surfaceMesh>& sf = tsf.ref();
Field<RetType>& sfi = sf.primitiveFieldRef(); // 境界面上で補間された値
const typename SFType::Internal& Sfi = Sf(); // 1
for (label fi=0; fi<P.size(); fi++) // 境界面上の値を補間
{
sfi[fi] = Sfi[fi] & (lambda[fi]*(vfi[P[fi]] - vfi[N[fi]]) + vfi[N[fi]]);
}最後に書かれている sfi[fi] = Sfi[fi] & (lambda[fi]*(vfi[P[fi]] - vfi[N[fi]]) + vfi[N[fi]]) が補間式(1)に該当する
surfaceInterpolationScheme の構造
surfaceInterpolationScheme では,まず引数として\(\phi\)と\(w\)をとり,境界面での補間を返す関数である interpolate() が呼ばれていると思われる
//- Return the face-interpolate of the given cell field
// with the given weighting factors
static tmp<GeometricField<Type, fvsPatchField, surfaceMesh>>
interpolate
(
const GeometricField<Type, fvPatchField, volMesh>&,
const tmp<surfaceScalarField>&
);
interpolate() の中では,さらに dotInterpolate(geometricOneField(), vf, tlambdas) を呼んでいる
template<class Type>
Foam::tmp<Foam::GeometricField<Type, Foam::fvsPatchField, Foam::surfaceMesh>>
Foam::surfaceInterpolationScheme<Type>::interpolate
(
const GeometricField<Type, fvPatchField, volMesh>& vf,
const tmp<surfaceScalarField>& tlambdas
)
{
return dotInterpolate(geometricOneField(), vf, tlambdas);
}.Hファイルのコメントから,vf が\(\phi\),tlambdasが重み係数\(w\)であると考えられる
geometricOneField() は\(1\)であり,非圧縮流れにおける密度などに使われる
Detailed Description
A class representing the concept of a GeometricField of 1 used to avoid unnecessary manipulations for objects which are known to be one at compile-time.
Used for example as the density argument to a function written for compressible to be used for incompressible flow.
Definition at line 55 of file geometricOneField.H.
OpenFOAM API Guide geometricOneField Class Reference
dotInterpolate() は surfaceInterpolationScheme.H で次のように定義されている
//- Return the face-interpolate of the given cell field
// with the given weighting factors dotted with given field Sf
template<class SFType>
static tmp
<
GeometricField
<
typename innerProduct<typename SFType::value_type, Type>::type,
fvsPatchField,
surfaceMesh
>
>
dotInterpolate
(
const SFType& Sf,
const GeometricField<Type, fvPatchField, volMesh>& vf,
const tmp<surfaceScalarField>& tlambdas
);
dotted with given field Sf の意味は分からないが,とりあえず引数として\(1\)と\(\phi\)と\(w\)をとり,境界面での補間を返す関数である
まとめ
OpenFOAMで実装されている離散化スキームである QUICK について解説した
↓その他の離散化スキーム
↓おすすめ記事

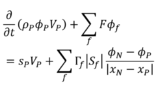





コメント